With the help of spectroscopy, the temperature and the components of a star can be immediately told. And after analysis, we will know much more.
The spectrum of the Sun is everywhere around us: rainbow in the sky, a beam in the dark room divided into different colors, to name a few. The Greek and Arabian astronomers noticed that in the ancient. But the first correct explanation of solar spectrum is made by Isaac Newton (1642-1722).
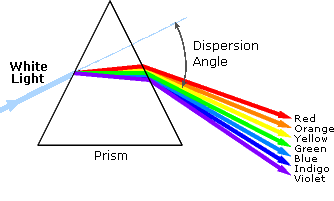
image from https://www2.chemistry.msu.edu/
The image above shows how Newton discovered spectra and how he used tool to study it. But due to the limit of technology, the resolution of Newton’s spectra was very low. That means he could tell much with the colorful beams he got. A lot of information was lost when the light was refracted.
Later, Joseph Fraunhofer (1787-1826) observed light with a small telescope behind a narrow slit and a prism. The dispersed light he observed had a better resolution. At that moment, he noticed the rainbow had many dark lines in it. But he cannot tell why.
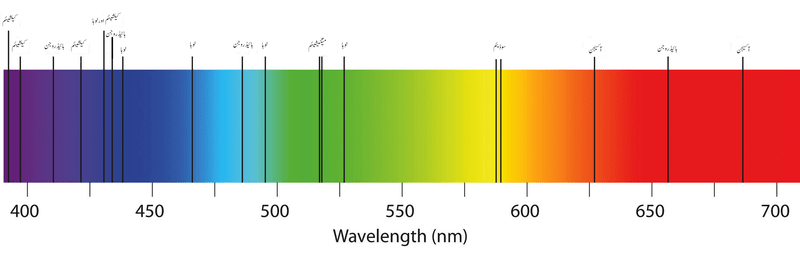
image from https://pediaa.com/difference-between-absorption-and-emission-spectra/
The secret of dark lines was discovered by Gustav Kirchhoff (1824-1887). Different chemical elements can absorb one or more particular kind of light (light in one particular wavelength). Which means if we figure out what element is absorbing the light in the dark region, we will know the components of a star. To explain more precisely, when a star in the sky is burning its fuel in its core (nuclear reaction like a nuclear bomb), all kinds of light are emited. But when the light is going through the surface of the star, some elements will absorb part of light, as we talk about before. so the light we see in our eye actually carrys lots of information about the star it comes from.